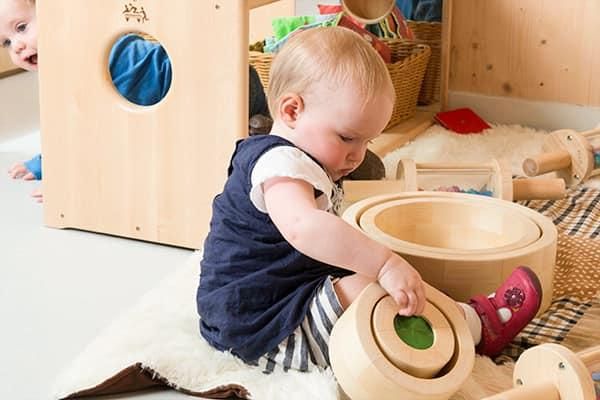
Many parents ask questions about nursery life and the types of learning that goes on… so here is an interesting insight into heuristic play – what it means and why we put this into our daily programmes.
Heuristic play is rooted in young children’s natural curiosity. As babies grow, they move beyond being content to simply feel and ponder objects, to wanting to find out what can be done with them. Toddlers have an urge to handle things: to gather, fill, dump, stack, knock down, select and manipulate in other ways. Household or kitchen utensils offer this kind of activity, as every parent knows, and can occupy a child for surprising stretches of time. When toddlers make an enjoyable discovery – for instance when one item fits into another, or an interesting sound is produced – they often repeat the action several times to test the result, which strengthens cognitive development as well as fine muscle control and hand/eye co-ordination.
In the book, People under Three, Elinor Goldschmied and Sonia Jackson coined the term heuristic play, to explain how to provide a more structured opportunity for this kind of activity. Heuristic play ‘consists of offering a group of children, for a defined period of time in a controlled environment, a large number of different kinds of objects and receptacles with which they play freely without adult intervention’. It is particularly useful for children in their second year who often seem unwilling to engage in any activity for more than a few minutes. According to the Oxford Dictionary, ‘heuristic’ means helping to find out or discover; proceeding by trial and error. It stems from the same root as Eureka – ‘I found it!’ Clare Crowther of Bridgwater College describes heuristic play as ‘an activity we use with one-year-olds, two-year-olds, and young threes, giving them the opportunity to experiment spontaneously with a wide range of non-commercial objects. Whilst the heuristic play session is in process, adults need to remain seated and quiet. This supports children in making their own choices and discoveries.’